This lab manual provides a comprehensive guide for understanding human anatomy and physiology through interactive exercises and detailed visual aids, ideal for nursing and allied health students.
1.1 Overview of the Lab Manual Structure
The lab manual is divided into six primary units, each focusing on different aspects of anatomy and physiology. It begins with an introduction to the field, followed by essential lab equipment and tools. Subsequent units cover human body systems, microscopic studies, practical exercises, and advanced learning topics. Each section includes detailed exercises, visual aids, and real-world applications, making it a versatile resource for both classroom and lab settings. The manual is designed to complement various textbooks and cater to students in nursing, allied health, and introductory courses.
1.2 Importance of Lab Work in Anatomy and Physiology
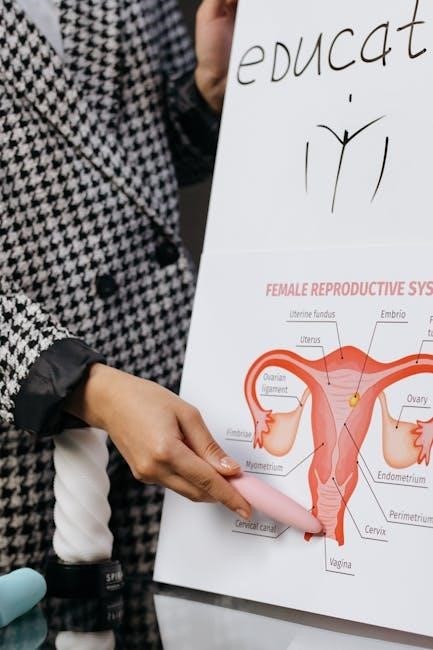
Lab work is crucial for bridging theory and practice, allowing students to explore anatomical structures and physiological processes hands-on. It enhances understanding of complex concepts through interactive activities and experiments, fostering critical thinking and practical skills. Labs also provide opportunities for applying knowledge in real-world scenarios, especially for nursing and allied health students. By engaging in experiments, students develop observation techniques, improve dexterity, and gain confidence in conducting scientific inquiries. This experiential learning reinforces textbook content, making anatomy and physiology more tangible and memorable for future professional applications.
Essential Lab Equipment and Tools
The anatomy and physiology lab requires microscopes, dissection tools, and safety equipment to ensure accurate tissue analysis and safe specimen handling, enhancing hands-on learning experiences.
2.1 Microscopes and Their Use in Histology
Microscopes are indispensable tools in anatomy and physiology labs, enabling detailed examination of tissues and cells. Compound microscopes are commonly used for histology, allowing students to study tissue structure and cellular details. Electron microscopes provide higher resolution for advanced observations. Proper use involves focusing, adjusting magnification, and preparing slides. Histology labs often involve staining techniques to enhance visibility of cellular components. Microscopes are essential for correlating tissue structure with physiological functions, making them a cornerstone of lab-based learning in anatomy and physiology courses.
2.2 Dissection Tools and Safety Protocols
Dissection tools, such as scalpels, forceps, and dissecting scissors, are essential for exploring anatomical structures. Proper safety protocols are crucial to prevent injuries. Students should wear gloves, lab coats, and goggles during dissection. Scalpels must be handled with care, and blunt tools are used for initial incisions. Preserved specimens may require specific handling to avoid chemical exposure. Safety training is mandatory before starting lab work. Tools must be stored correctly and sterilized after use to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination. Adhering to these protocols ensures a safe and effective learning environment for anatomy and physiology students.

Human Body Systems Covered in the Lab Manual
The lab manual explores the integumentary, skeletal, nervous, and muscular systems, providing a comprehensive study of their structures, functions, and interconnections within the human body.
3.1 Integumentary System: Skin Structure and Function
This section focuses on the integumentary system, detailing the structure and functions of the skin. It covers the layers of the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, as well as skin appendages like hair, nails, and glands. The manual explains how these components work together to protect the body, regulate temperature, and maintain homeostasis. Through diagrams and lab exercises, students learn to identify skin features under a microscope and understand its role in overall health. This chapter provides a foundational understanding of the integumentary system, essential for nursing and allied health professions.
3.2 Skeletal System: Bones and Joints
This section explores the skeletal system, focusing on the structure and classification of bones, including long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid bones. It details bone tissue composition, such as compact and cancellous bone, and explains the process of bone formation and remodeling. The manual also covers the types of joints, including synovial, cartilaginous, and fibrous joints, and their roles in movement. Lab exercises include identifying bones and joints through dissection or models, and analyzing radiographs to understand skeletal health. This chapter provides a hands-on approach to understanding the skeletal system’s role in support, protection, and movement.
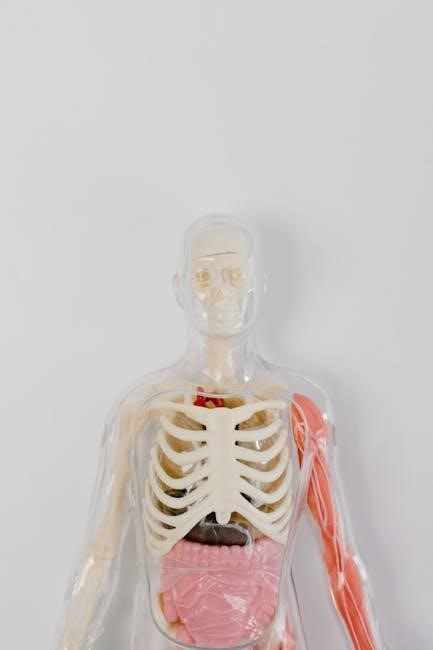
Microscopic and Histological Studies
This section focuses on examining tissues and cells under a microscope, providing insights into histological structures and their functions, essential for understanding human anatomy and physiology.
4.1 Examining Tissues and Cells Under a Microscope
Examining tissues and cells under a microscope is a fundamental skill in anatomy and physiology. This section guides students through preparing slides, focusing specimens, and identifying cellular structures. Compound microscopes are used to study tissue samples, while stereo microscopes provide 3D views of larger structures. Students learn to differentiate between various tissue types, such as epithelial, connective, and muscular tissues, and understand their functions. Histological staining techniques are introduced to enhance visibility of cellular details. Practical exercises include identifying organelles and understanding the hierarchy of structures, from cells to tissues and organs. This hands-on approach reinforces theoretical concepts and improves observational skills. Proper safety protocols are emphasized to ensure safe handling of equipment and specimens.

4.2 Identifying Organs and Their Functions
This section focuses on recognizing major organs and understanding their roles within body systems. Students learn to identify organs such as the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys through detailed diagrams and dissection activities. The lab manual emphasizes the relationship between organ structure and function, using histological slides to explore internal anatomy. Interactive exercises, like matching games and labeling quizzes, reinforce organ identification skills. Additionally, comparative anatomy studies highlight differences between human organs and those of other species, enhancing comprehension of evolutionary adaptations and functional diversity. This practical approach helps students connect anatomical knowledge to physiological processes.
Practical Exercises and Activities
Engaging exercises and hands-on activities enhance learning, including simulations, group work, and real-world applications, helping students apply anatomical knowledge to practical scenarios effectively.
5.1 Interactive Labs for Physiology Concepts
Interactive labs provide dynamic ways to explore physiology, featuring simulations, group activities, and hands-on experiments. These labs allow students to visualize complex processes, such as nerve impulses and muscle contractions, in real-time. By engaging with digital tools and collaborative tasks, learners gain a deeper understanding of how body systems function. Practical exercises include measuring physiological responses, analyzing data, and applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios. Such interactive approaches enhance retention and critical thinking, making physiology concepts more accessible and memorable for students at all levels of study.
5.2 Applied Anatomy for Nursing and Allied Health
This section focuses on practical applications of anatomy for nursing and allied health professionals. It emphasizes internal and surface anatomy, crucial for patient care. Exercises include identifying anatomical landmarks, understanding surgical sites, and correlating structure with function. Activities simulate clinical scenarios, preparing students for real-world practice. The manual highlights regions relevant to common medical procedures, ensuring a strong foundation for healthcare professionals. These applied labs bridge theory and practice, fostering competency in patient assessment and treatment planning. They are designed to enhance clinical reasoning and procedural skills essential for nursing and allied health careers.

Specialized Lab Units for Advanced Learning

Advanced lab units focus on specialized topics like the nervous system, sensory experiments, and muscular structure. These units provide in-depth studies and complex experiments for enhanced learning.
6.1 Nervous System and Sensory Experiments
This unit delves into the structure and function of the nervous system, focusing on sensory organs and neural mechanisms. Students explore reflexes, nerve impulses, and sensory perception through hands-on experiments. Key activities include dissecting neural tissues, analyzing nerve cell histology, and conducting sensory testing to understand how stimuli are processed. These labs emphasize the integration of anatomy and physiology, providing a deeper understanding of how the nervous system regulates body functions and responds to environmental changes. Practical exercises also cover the microscopic examination of neurons and glial cells, enhancing comprehension of neural communication.
6.2 Muscular System: Structure and Movement
This section explores the muscular system’s role in movement and support. Labs focus on the histology of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, highlighting their structural differences. Practical exercises include muscle dissection to identify origins, insertions, and actions. Students analyze muscle physiology, such as contraction mechanisms and nerve-muscle interactions. Activities emphasize how muscles work in groups to produce precise movements. Additionally, experiments on muscle fatigue and recovery demonstrate physiological responses to activity. These hands-on experiences provide a comprehensive understanding of how muscles contribute to locomotion, posture, and overall bodily functions.